Magnets and Lithium-ion Batteries Attention
Dec 11, 2019 Pageview:3579
Three things are most important for battery users and manufacturers: performance, long service, and safety. Well, if you want to get the best out of your battery, you may have to sacrifice one and focus on two of these factors. That is for small devices like smartphones and similar instruments. For larger applications like EVs, however you may want all three elements working correctly.
There have been several pieces of research by different stakeholders to try and improve battery performance. In one case, scientists demonstrated the role magnets could plant in aligning graphite flakes inside the electrodes. From the recent publication in Nature Energy, magnetic alignment can create a clear path for lithium ions. As a result, the batteries achieve better performance.
Lithium-ion is one of the most powerful battery chemistries in the world. It has been used to run most of the powerful devices. And with the emergence of electric vehicles, their production has almost tripled over the last few years. So what is the effect of magnets on these batteries?
Does proximity to magnets damage or affect lithium-ion batteries?
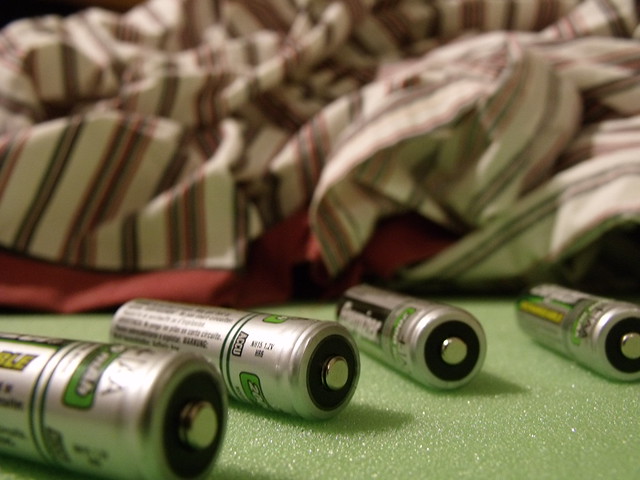
If you have any Smartphone, laptop, or power bank in your house, you are probably running on a Lithium-ion battery. The technology has become common in these devices. Other devices like drones use updated Lithium-ion batteries like Lithium Polymer.
The point is, Lithium-ion batteries are more common today than any other cell. There use has become paramount for almost every device. They are loved because they are sturdy and last longer. They have a higher capacity, making them unique for high-drain devices. And now the world of E-bikes and EVs has taken them to a higher level.
However, there comes a time when you may feel our laptop is not giving you the performance you expect. And perhaps you have noticed they are influenced more by their proximity to the magnets. For many people, the most probable course of action would be to replace them. Now before you do this, there are a few things you should know first.
Li-ion batteries are made with two primary ingredients, Lithium and Carbon/Graphite. Lithium is an alkali metal, which means it is not magnetic. When you add a magnetic charge to lithium, it will not make and difference.
There is also carbon inside lithium-ion batteries. The carbon is rated in a low-grade magnetic field. Because of this, the magnet in your home does not affect the battery’s performance.??
?However, high power magnets like those used for scientific testing can affect your lithium-ion batteries. This is why you are not allowed to enter a testing environment with your electronic device. There are other powerful magnets, the Neodynamic silver magnets that can be trouble for your batteries, but they are scarce.
There have been several scientific studies for Li-ion and magnets to try and improve performance. In the results, magnets can be used to improve performance whereby magnetic fields align carbon and graphite flakes. This process happens within the electrodes during the initial manufacturing process. Lithium ions, therefore, get a clear path to move from the anode to the cathode and vise Versa. In a nutshell, internal resistance is reduced.
Battery performance is not about changing materials to come up with better batteries. Today, the main focus is on changing older technologies to improve them. In the case of magnets, there is no adverse effect on Li-ion cells. On the contrary, they can be used to enhance their performance.
Is lithium-ion battery magnetic?
To answer this question, we need to understand the components in a lithium-ion battery. We have already mentioned that there are two primary components in the cells; lithium and carbon.
Lithium. This is one of the lightest metals. It gives lithium-ion batteries the ability to have more capacity. The metal is alkali in nature, which means it does any effect on magnets. At the same time, the metal is not affected by a magnetic presence. You can, therefore, keep your batteries near magnet at home and still get the best performance.
Carbon. This component is propylene carbonate. The organic mixture has the lowest magnetic field rating. Many magnets at home are very low rated as well. You will need something powerful to affect this amount of rating. But for high-end magnets, you should expect them to hurt the performance of Li-ion batteries.
In conclusion, older technologies of lithium-ion batteries are not magnetic. In recent times, however, researchers are using magnetic fields to align carbon graphite flakes in the electrodes, a process that takes place during manufacture. This means newer lithium-ion batteries should have magnetic properties which give them more power.
How do you protect lithium-ion batteries by magnetism control?
Magnetization is one of the most exciting fields studied today. It is essential, especially in the current flow.
It is defined as the manipulation of magnetism employing voltage actuation. The subject has been studied for an extended period for several applications.
Lithium-ion batteries LIBs have experienced rapid development over the past few years. The electrode material is used as a way of inserting lithium atoms. The current flow of the battery directly affects the electrochemical reaction.
Lithium-ion insertion has become a significant cause of changes in magnetic properties. Adjustment of discharge has achieved the rechargeable nature of LIB.
Different researches have been carried to try and increase battery performance. Lithiation/delithiation process repeated as a result of magnetization/demagnetization.
Due to the nature of its components, LIBs require extended discharge. Reversible magnetization can be used to achieve voltage tuning.
In conclusion, magnetism can be achieved through LIB cycling. This process seems long, but the user can make it of expert knowledge in a set environment. The aim is to give LIB a better life as well as ensuring the proper distribution of power.
Lithium-Ion battery remains to be the most popular chemistry among technology devices users. It is, therefore, essential to understanding how different situations affect the batteries.
- Prev Article: Lithium-ion Battery Anode and Cathode Explanation
- Next Article: Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO) Battery - LiMn2O4 Manufacturer
Leave Message
Hottest Categories
-
Hottest Industry News
-
Latest Industry News